Introduction
Released in November 2020 by fiatjaf, Nostr is an open, decentralised, censorship-resistant messaging protocol. The protocol is well designed, and many authors have written extensively about the mechanics and use-cases. For the purposes of this article, I will narrow the focus to Nostr as a tool to enable the creation of platform markets. My aim is to give the reader an introduction to platform market pricing and provide concrete steps to price their platform strategically.
What is a Platform Market?
A platform market consists of multiple groups of users who want to interact but can’t do so directly. The platform brings them together to enable interaction, benefiting all users and the platform itself by enabling these interactions and pricing appropriately. Although platform markets have been around forever, the last decade has seen an explosion in their number due to the ubiquity of the internet.
Examples:
· YouTube
· TV
· Twitter (X)
Platform markets have historically earned significant revenue if they design their pricing correctly. This is because platform markets don’t need to produce goods themselves; rather, one or more “sides” of the platform produce goods and services for the other side, with the platform merely enabling the exchange. TikTok is a prime example: it produces nothing except a video hosting service, with users generating all the content for other users. Effectively, the platform has only fixed costs and very low marginal costs.
Therefore, platform markets are far more scalable than traditional one-sided markets, as their primary concern is to attract as many users as possible (who have no marginal cost to the platform). Additionally, platforms often enjoy a captive audience, making it difficult for competitors to entice away users once they are established. This is particularly evident in software and payment platforms.
How Does Nostr Enable the Creation of Platform Markets?
· Open Protocol: Like the internet, Nostr is an open protocol.
· Inbuilt Payment Systems: Nostr integrates payment systems such as Bitcoin’s Lightning Network.
· Existing User Base: It already has a growing user base.
· Decentralisation: This feature acts as a moat against competitors.
Types of platform enabled by Nostr
As of 2024 we are seeing multiple types of platforms that Nostr has enabled. The first is Nostr relays. A Nostr relay is a simple server that receives and broadcasts user notes (messages) in the Nostr protocol. Users can publish and fetch notes across multiple relays. Nostr relays can be configured by their operator to curate content on specific topics or people. Alternatively, they can be configured with an algorithm as experienced by users of contemporary social media. These can be valuable for users. And potentially, paid relays are a viable business opportunity.
The second platform Nostr enables is the Nostr client. Nostr clients are analogous to internet browser software. Historically, we have seen users be charged to install an internet browser, though this is unlikely to emerge in the market for Nostr clients. As a platform, a Nostr client might be bundled with a relay service (with curation or algorithm).
The third type of platform is Nostr apps. Each app can be designed as a platform if that is valuable for users. We are already seeing Nostr-based alternatives for music and video streaming, looking to compete with apps like YouTube.
We can’t know what the future will hold but the possibilities for designing platforms with Nostr are many. The advantage in designing a platform is that you can create a two sided market.
What is a Two-Sided Market?
All two-sided markets are platform markets, but not all platform markets are two-sided markets. The critical aspect of a two-sided market is that the volume of interactions on the platform depends on both the relative prices charged to each side and the total price charged. This is the case when both sides value more users on the other side, known in literature as an “indirect network externality.”
An example of a one-sided platform market is a clothes retailer, where the volume of sales depends only on the total price, not the relative prices charged to buyers and producers. Conversely, YouTube is a two-sided market where both creators and watchers benefit from more users. Watchers benefit from more variety and quality, while creators benefit from more users and views. YouTube introduces a special category of creators, the advertisers, who benefit monetarily from views because consumers viewing their content are likely to purchase their goods.
The prices paid by YouTube users are not all monetary:
· Watchers are charged an inconvenience fee in the form of advertisements.
· Advertisers are charged a monetary fee.
· Creators are not charged any fees.
Let’s assume the total fees for YouTube add up to $100. Say advertisers are charged $90, watchers face an inconvenience worth $10, and creators still enjoy $0 costs. In this scenario, the total volume of videos watched might be some number like 100,000.
Assume we change the price structure to advertisers being charged $80, watchers paying an inconvenience worth $10, and creators being charged $10 (keeping the total fees at $100). In this new scenario, the likely outcome is that the marginal creator will no longer create videos, and thus, the total volume of videos watched will fall.
Two-Sided Markets that Allow Money Exchange
The key to understanding Nostr’s value lies in its inbuilt payment mechanism—Bitcoin’s Lightning Network protocol. Although this protocol is not part of the Nostr codebase, the existing Nostr clients incorporate it to allow users to pay each other bitcoin with a simple user interface. This means that Nostr as a protocol is ideal for creating platforms where users can exchange monetary value. The mechanics and design choices of the Lightning network further augment Nostr’s value proposition more so than traditional payment systems like credit cards, PayPal, etc.
Key Problem: Chicken and Egg
So far, we have established that platform markets enable at least two groups of users to come together and exchange. The primary problem is that both groups will only use the platform if the other group is already using it, creating a classic chicken and egg scenario. Platforms operate by bringing groups of users together, making users reticent to switch to a new platform because they don’t know if the other users will be there. This gives existing platforms enormous power.
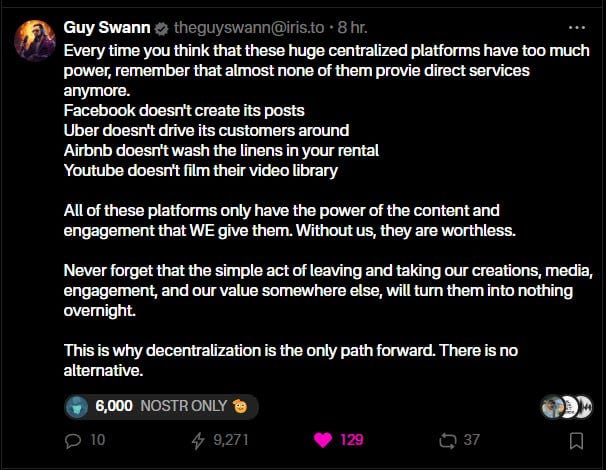
Guy Swann sums this up well in this Nostr note: note1695j0czewtkfwy7h4ne7k2ug706uwc7lendsq50prsfp8vwq8nfszdx4z7.
Competing with Existing Platforms: Divide and Conquer!
To compete with existing platforms, you need to divide and conquer. The original formulation for this strategy is given in both Caillaud and Jullien (2003) and Armstrong (2006). To take advantage of the indirect network externalities identified earlier, the divide and conquer strategy involves subsidising one side of the market to attract a large user base (the "divide" part) and then monetising the other side of the market (the "conquer" part).
Divide: Attract one side of the market by offering lower prices or subsidies. For example, offer free registration to one side. This subsidy is essential to kickstart the network effects, as a larger user base on one side increases the platform’s attractiveness to the other side. This was observed in the early days of YouTube, which was free for both creators and watchers.
Conquer: Once a substantial user base is established on the subsidised side, charge higher fees on the other side of the market. This can be seen in contemporary YouTube, where advertisers (a specific kind of creator) pay fees, and watchers deal with the inconvenience of watching ads (inconvenience is a non-price fee).
Implementing This Strategy in Your Platform:
So who are are you dividing, who are you conquering? Deciding which side to subsidise involves understanding which side offers more benefit to the other side. For example, in nightclubs (Wright, 2004), men and women go to interact. Men are assumed to gain more from each woman’s presence than vice versa, so nightclubs often subsidise women with free entry or drinks to attract men.
First, consider all your user groups. What brings them to your platform, what do they want to gain by interacting with the other user groups.
Think about, and identify, which group confers more value for the other group by being on the platform.
Then, think about how you can subsidise that user group. Free access is common. But Nostr allows seamless payment integration which encourages users to exchange money. A potential model for your platform could be that you charge a fee to both users based on how much value they send to each other. One way to subsidise users in this case is to reduce those fees.
Alternatively, you could pay users to join your platform using Nostr’s integration with the Lightning Network.
References:
· Armstrong, M. (2006). Competition in two-sided markets. The RAND Journal of Economics, 37(3), 668-691.
· Caillaud, B., & Jullien, B. (2003). Chicken & Egg: Competition among Intermediation Service Providers. The RAND Journal of Economics, 34(2), 309-328.
· Wright, J. (2004). One-sided logic in two-sided markets. Review of Network Economics, 3(1).